We take pride in working with industry leaders who trust our expertise. In every project, we deliver quality, sustainability, and long-lasting solutions.
At Senkron Surface Technologies, we develop coating processes optimized for each application area based on modern manufacturing techniques and international standards. By offering customized solutions tailored to our customers’ needs, we enhance surface durability and provide sustainable added value to production processes.
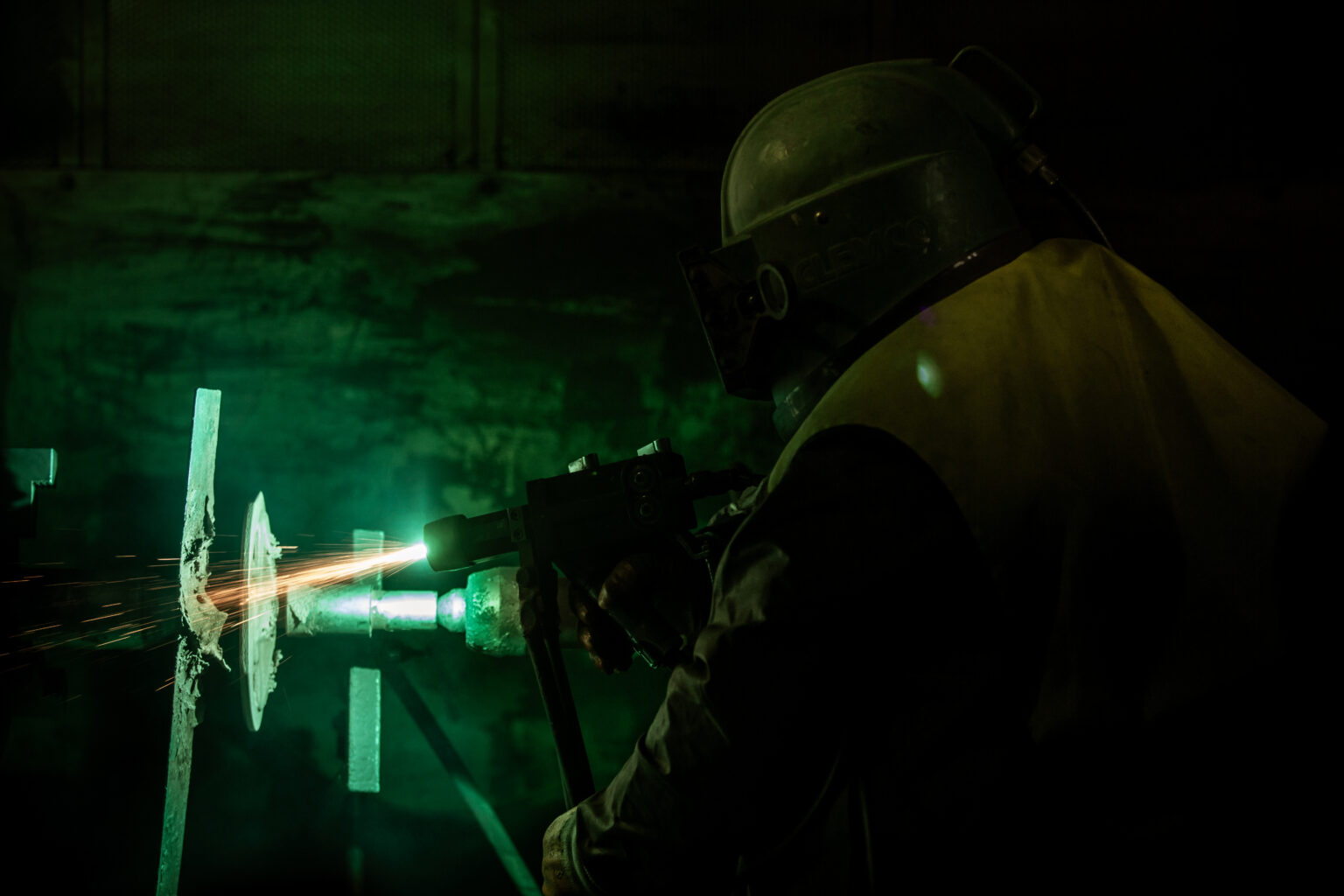

Micro-pulverized alloy powders are sprayed onto the surface to be coated through the center of an oxy-acetylene flame under vacuum with oxygen. Since the temperature of the part does not exceed 200°C during coating, this method is referred to as a cold system.
The flame temperature is approximately 3300°C. Adhesion is mechanical. Coating thickness varies between 0.05 and 2.5 mm depending on the material being sprayed and the shape of the workpiece. The adhesion strength ranges from 600 to 1000 PSI, and surface roughness is between 10% and 20%.
This method can be defined as spraying any metal wire—whose melting point is below the temperature of the oxy-acetylene flame—onto the surface to be coated. The metal wire to be sprayed is fed by a wire driver into the nozzle of the spray gun, where it is melted by an oxygen and fuel gas flame as it passes through the nozzle. The molten metal is then atomized with high-pressure air and sprayed onto the surface to be coated.
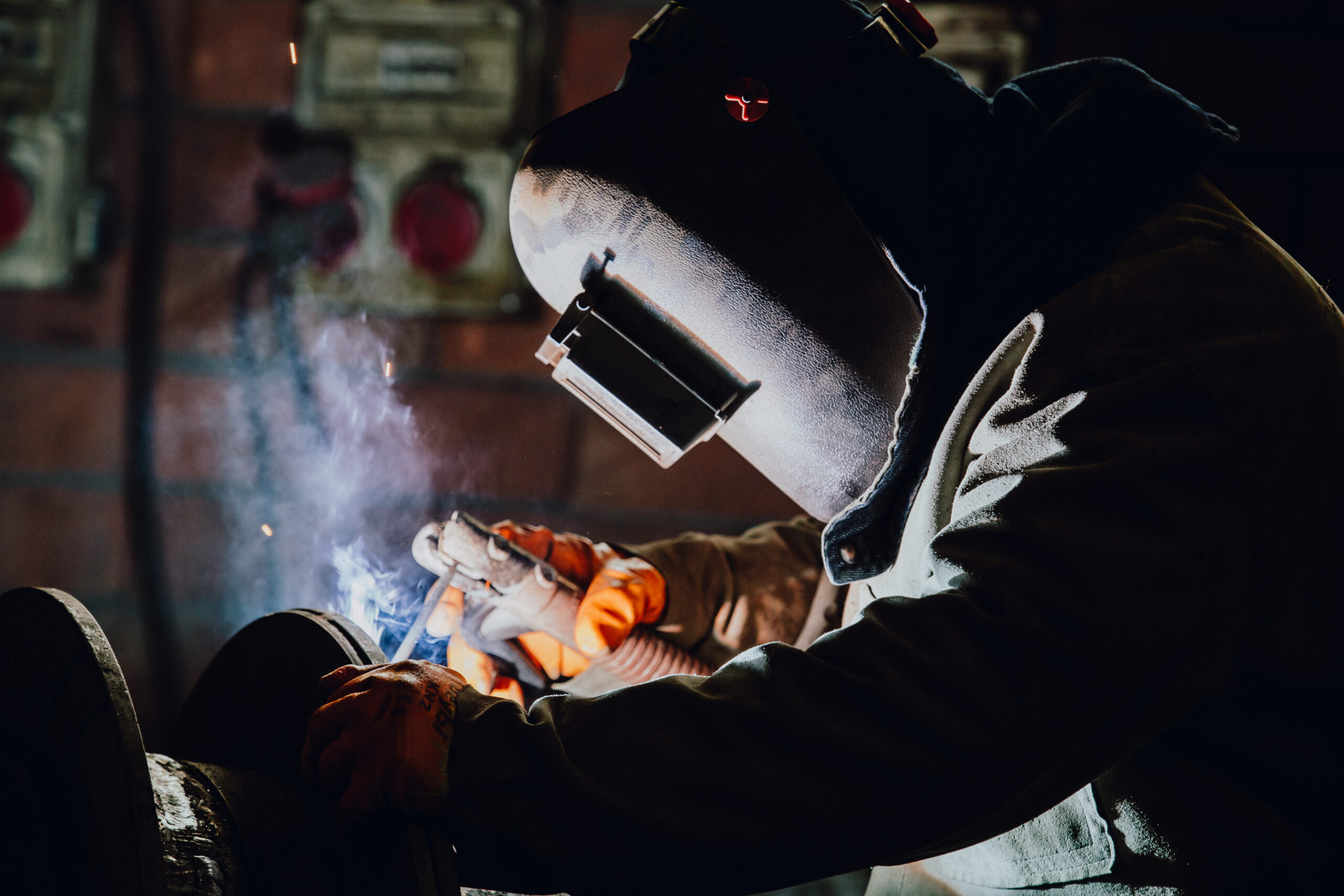


This is a suitable method for spraying metals in wire form. The spray wires are fed into the spray gun using an electric motor. When the wires, charged with positive and negative poles, come into contact with each other at the nozzles, an arc is formed. Through this arc, the metal melts and is atomized with compressed air onto the prepared surface. The temperature of the arc is approximately 4000°C.
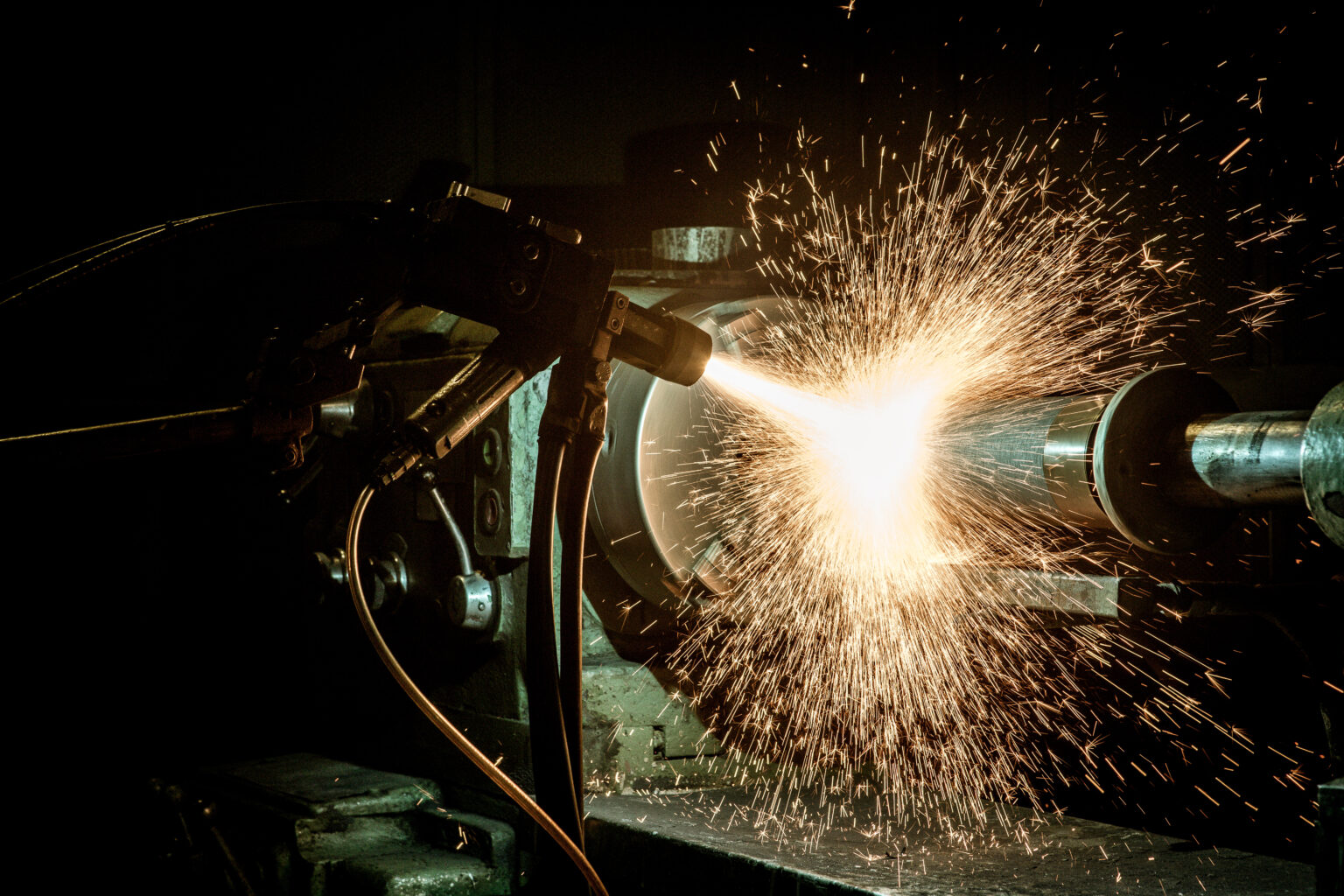
In the combustion chamber of a high-speed HVOF gun, gaseous fuels (such as Propane, MAP, Propylene, or Hydrogen) burn continuously with oxygen. The fuel gas pressure can vary between 60–90 PSI, which allows for control over spray velocity and enables the creation of dense and hard coatings. The flame temperature ranges between 2500–3000°C, and particle velocity ranges from 350 to 1000 m/s. Coatings produced by this process have a higher bond strength compared to plasma spraying. Coating thickness varies depending on the application and typically ranges from 0.05 to 1.5 mm.
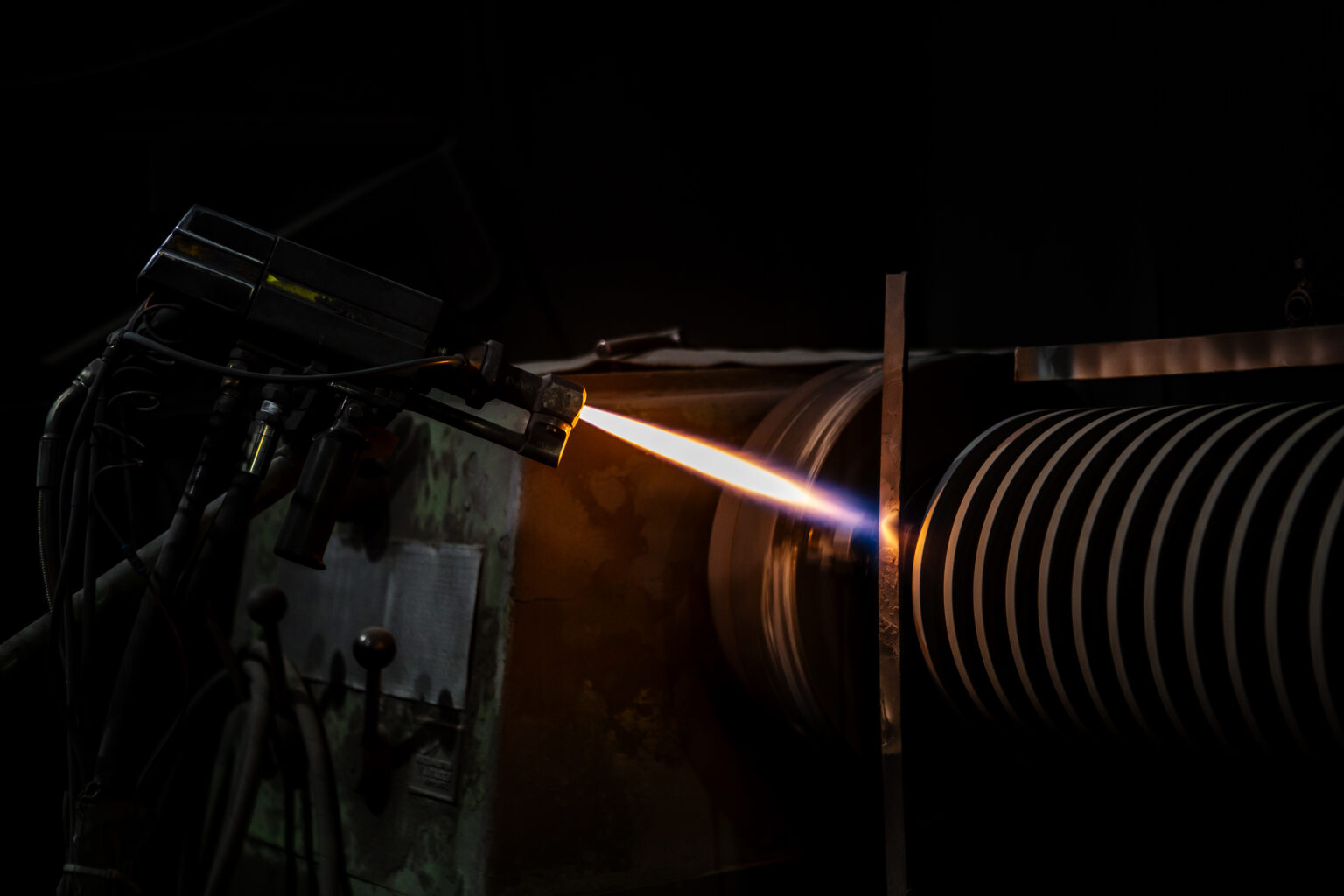

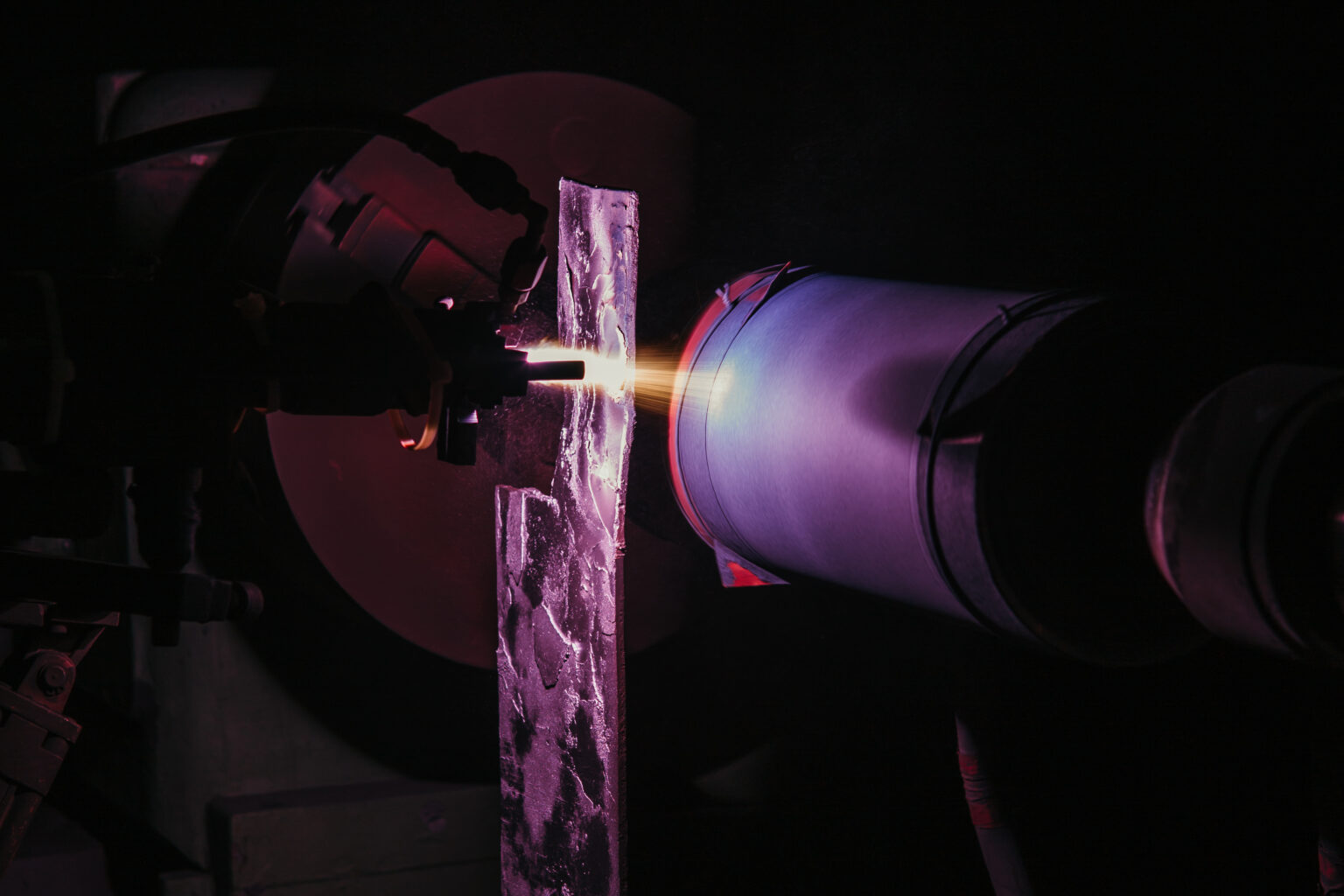
In this process, diatomic gases (a mixture of Argon and Hydrogen) are ionized by an arc generated between a Tungsten cathode (-) and a copper nozzle (+). These gases reach plasma temperatures ranging from 15,000°C to 25,000°C, and the coating powders are sprayed onto the substrate material at this extremely high temperature. Compared to flame spraying, plasma spraying allows for denser coatings with a longer service life. Bond strength ranges from 5,000 to 10,000 PSI, and surface roughness is 5% or less.
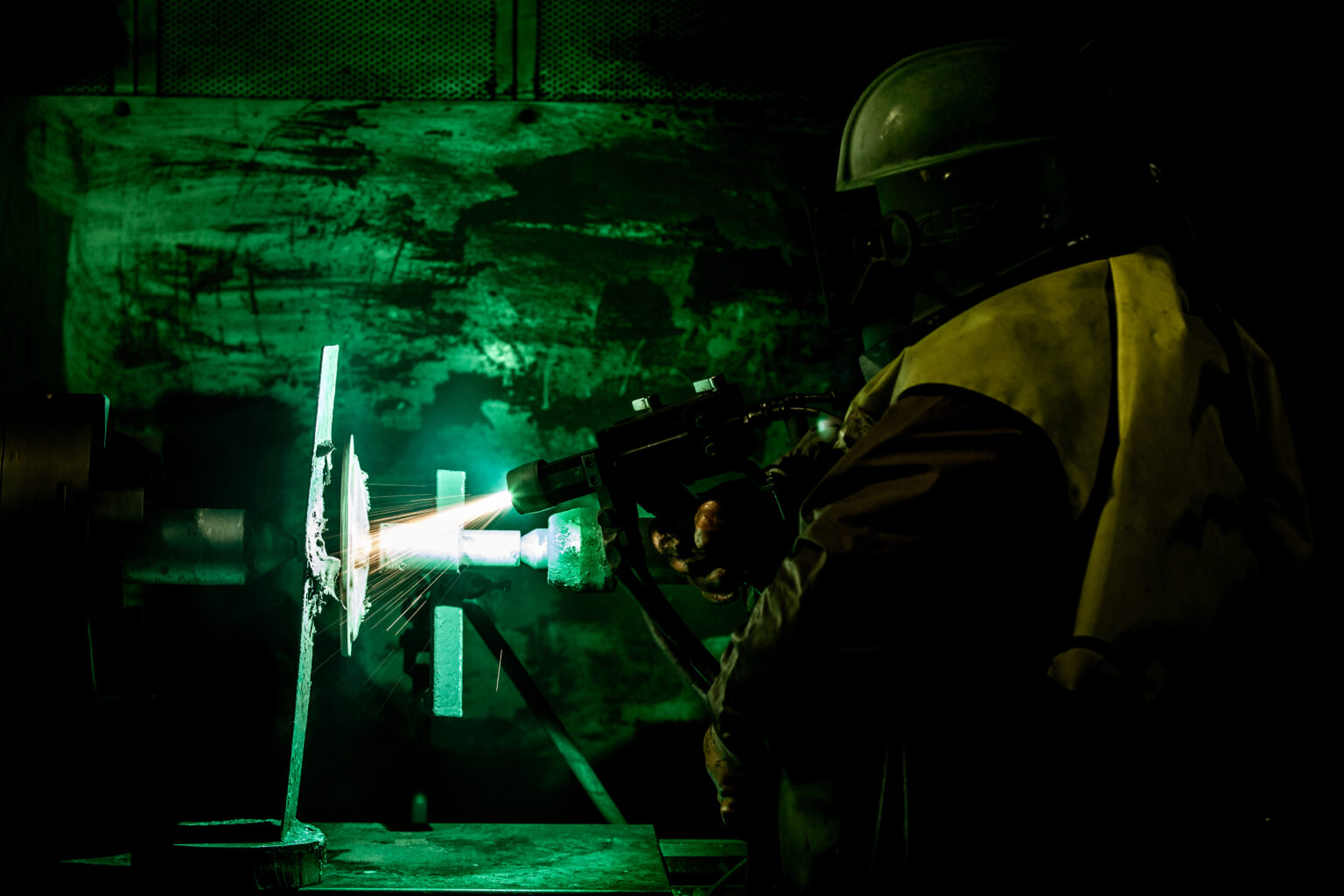
PTA is a plasma arc welding technique performed with continuous powder feeding. Powder can be fed either directly through the center of the nozzle or externally. The arc is generated between a tungsten electrode and the workpiece. Ignition begins with a pilot arc between the tungsten electrode and the copper nozzle (anode). Both the main arc and the pilot arc are powered by a control unit.
Argon gas is supplied around the tungsten electrode. As it passes through the arc, the gas becomes ionized and transforms into a high-energy plasma flame. A shielding gas mixture is supplied around the outer nozzle wall to protect the weld pool from oxidation. The powder is introduced into the arc, carried by Argon gas, and directed into the weld pool.
PTA is particularly effective for welding alloy powders that cannot be formed into wire or rods. The key advantage of this method is its precise control over weld penetration and thickness, making it ideal for porosity-free, uniform welds and automation due to its continuous powder feed system.

We take pride in working with industry leaders who trust our expertise. In every project, we deliver quality, sustainability, and long-lasting solutions.
With our high-tech coating solutions and sectoral expertise, we create value across every field of industry.
At Senkron Surface Technologies, we are committed to quality, innovation, and sustainability, delivering durable, reliable, and environmentally conscious services to our clients.
AKSE MAH. 534 SOK.NO:3 GÜZELTEPE ÇAYIROVA / KOCAELİ TÜRKİYE
Stay updated with our latest news and events — sign up now.
Copyright © 2025 Senkron Yüzey Teknolojileri by Global Media Factory. All Rights Reserved.